Hydrophobic Molecules Usually Enter a Cell via
Endocrine glands secrete _____. The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide and hydrophobic molecules such as lipids to pass through the cell membrane down their concentration gradient by simple diffusion.

Mechanism Of Lamellar Body Formation By Lung Surfactant Protein B Sciencedirect
Entry of a moleculeparticle into the cell can be through various mechanisms like endocytosis pinocytosis direct.
. Question 159 1 1 point Small nonpolar hydrophobic molecules such as fatty acids easily pass through a membranes lipid bilayer. Is diffusion more rapid or more slow in cells with microvilli compared to cells lacking microvilli. The function of nucleolus is to make.
- A gradient is followed for this movement and once the concentration of both the solutionson either sides of. The major source of energy for mammalian cells is glucose. Hence non polar molecules like steroid hormones gain entry into the cell through the process of diffusion.
Very slowly diffuse through a membranes lipid bilayer. You are a scientist observing a membrane through which water and some small hydrophobic molecules can freely pass along a concentration gradient from high to low. However some sugar molecules are too large to pass through the membrane either way without the assistance of passive transport proteins.
Nanomaterials such as druggene delivery carriers usually enter the cell via penetration. Glucose entry into the cell is by _____. Hydrophobic molecules usually enter a cell via _____.
The cell membrane can filter out unimportant molecules that the cell does not need to use and also only lets small molecules pass through. Hydrophobic molecules usually enter a cell via _____. Figure 313 Simple Diffusion Across the Cell Plasma Membrane.
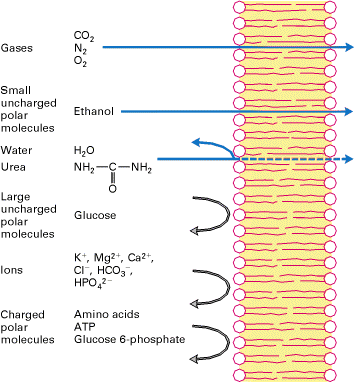
Thus gases such as O 2 and CO 2 hydrophobic molecules such as benzene and small polar but uncharged molecules such as H 2 O and ethanol are able to diffuse across the plasma membrane. In eukaryotic cells organelles are formed inside of cells from smaller sacs created from phospholipid bilayers. The osmotic pressure exerted by a cell would decrease if the cell synthesized more proteins.
How do water molecules move through hydrophobic cell membranes. Hydrophobic molecules usually enter a cell via _____. The plasma membrane has a hydrophobic environment in its interior.
Molecules that are hydrophobic can easily pass through the cell membrane if they are small enough because they are water-hating like the interior of the membrane. Diffusion is more rapid in cells with microvilli compared to cells lacking microvilli. The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide and hydrophobic molecules such as lipids to pass through the cell membrane down their concentration gradient by simple diffusion.
Integral membrane proteins enable ions and large polar molecules to pass through the membrane by passive or active transport. The NaK pump creates a _____ charge inside the cell. Usually enter the cell via endocytosis.
If the concentration of glucose in the water outside of a cell is higher than the concentration inside. Charged atoms or molecules of any size cannot cross. Glucose entry into the cell is by facilitated diffusion.
Endocrine glands secrete _____. - Osmosis is the process in which a solvent moves from a solution of low concentration to a solution of higher concentration. The water molecules move across the cell membrane by travelling along the concentration gradient of the solution low to high.
Hydrophobic molecules usually enter a cell via___________. Sugars pass through the cell membrane without the aid of proteins. Very small polar molecules such as water can cross via simple diffusion due to their small size.
Hydrophobic molecules and small polar molecules can diffuse through the lipid layer but ions and large polar molecules cannot. The hydrophobic sequences of DNA can provide a driving force for penetration. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable.
Figure 313 Simple Diffusion Across the Cell Plasma Membrane. The structure of the lipid bilayer allows small uncharged substances such as oxygen and carbon dioxide and hydrophobic molecules such as lipids to pass through the cell membrane down their concentration gradient by simple diffusion. The rate of diffusion increases as the concentration gradient increases.
3 Simple Diffusion Across the Cell Plasma Membrane. For example the DNA-LDH-DNA sandwich complex will be gradually inserted into the membrane to minimize exposure of the DNA hydrophobic sequences in the hydrophilic solvent. Cells have a variety of special proteins embedded into the membrane which help transport hydrophilic molecules like water and ions across the hydrophobic middle portion of the membrane.
Require transport proteins to pass through a membranes lipid bilayer. Are actively transported across cell membranes. Molecules that are entering or exiting the cell can diffuse via passive transport.
Water will tend to leave the the cell by osmosis. Small lipids and steroids are hydrophobic and can readily cross the membrane. Importantly only small relatively hydrophobic molecules are able to diffuse across a phospholipid bilayer at significant rates Figure 1215.
Only molecules that are entering the cell from the outside can diffuse via passive transport. Hydrophobic signaling molecules dont like water and are able to diffuse directly through the membrane where they bind to receptors inside the cell.
How Can A Non Polar Molecule Pass Through Cell Membrane Quora

Cell Signaling The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

What Is Facilitated Diffusion To Assist The Transport Of Sugar And Sodium Molecules Quora

Cell Membrane Midterm Topic 3 Flashcards Quizlet

Phyllis Webb Phylliswebb5sk Teaching Biology Medical School Studying Biology Lessons

Lecture 1 Outline Ch 5 I Membrane Structure Ii Permeability Ppt Video Online Download

Membrane Transport Of Small Molecules And The Electrical Properties Of Membranes Mb 207 Molecular Cell Biology Part Iii Internal Organization Of The Ppt Download

A Versatile Platform For Generating Engineered Extracellular Vesicles With Defined Therapeutic Properties Molecular Therapy

Second Messenger Biology Britannica

The Heat Shock Response Life On The Verge Of Death Molecular Cell

Comments
Post a Comment